This comprehensive guide will explore the importance of configuration testing for actuator performance, delve into the key components of actuator control systems and motors, and provide a step-by-step guide for actuator test procedures. By the end, you will thoroughly understand how to master AUMA actuator configuration testing for optimal performance.
Introduction
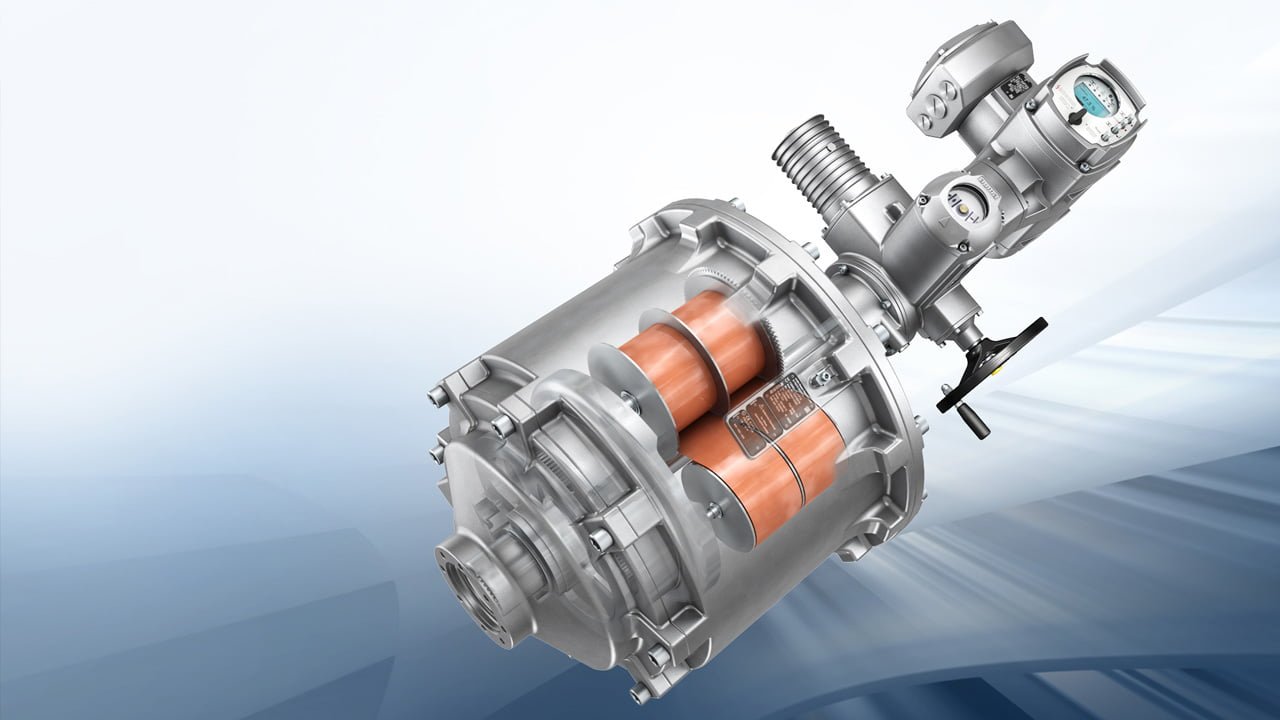
AUMA actuators are renowned for their quality and reliability in valve automation. They offer a wide range of electric actuators for various applications, including water and wastewater treatment, power plants, and industrial processes. As a critical component in valve control, AUMA actuators play a vital role in ensuring these systems’ efficient and safe operation.
Given their importance in maintaining the functionality of various systems, it is crucial to ensure that AUMA actuators are configured and tested correctly. Proper configuration testing ensures that the actuators operate at optimal performance, ultimately saving time and money by reducing the likelihood of system failures and costly downtime.

Importance of Actuator Configuration Testing for Performance
Configuration testing is an essential aspect of maintaining optimal actuator performance. This process systematically checks various settings and parameters to ensure the actuator functions correctly and efficiently. By conducting regular configuration testing, operators can identify and address potential issues before they escalate into more significant problems, which can lead to system downtime and increased costs.
In addition to ensuring optimal performance, configuration testing is crucial for maintaining the safety of a facility’s operations. Actuators are often responsible for controlling the flow of hazardous materials or ensuring the proper functioning of safety systems. By regularly testing and configuring actuators, operators can mitigate the risk of accidents caused by malfunctioning equipment.
Moreover, configuration testing can improve the overall lifecycle of an actuator. By identifying and addressing issues early on, operators can prolong the lifespan of their equipment and reduce the need for costly replacements. In the long run, this can lead to significant cost savings and increased efficiency for the entire system.
Understanding Actuator Control Systems
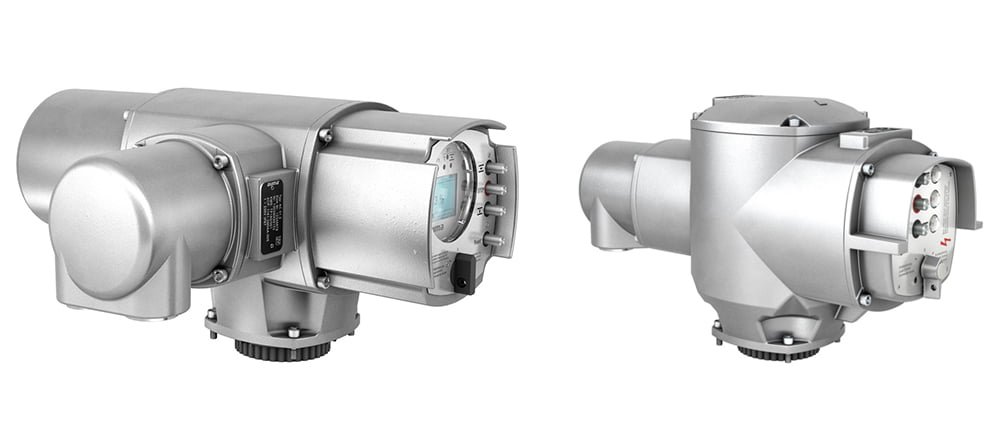
Actuator control systems are essential for managing the operation of AUMA actuators. These systems typically consist of an actuator controller, which communicates with the actuator motor and any necessary sensors. The controller is responsible for interpreting input signals, processing them, and sending output signals to the actuator motor to execute the desired action.
There are various actuator control systems, each with unique features and capabilities. Some common examples include:
1. Local Control Stations (LCS):
These standalone control systems allow operators to control actuators locally. They typically include pushbuttons, switches, and indicators for manual operation and monitoring.

2. Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs):
PLCs are more advanced control systems that can be programmed to execute complex operations and sequences. They can communicate with multiple actuators and other devices, making them suitable for large-scale systems.
3. Distributed Control Systems (DCS):
DCS are comprehensive control systems integrating multiple subsystems, including actuators, sensors, and other devices. They offer centralized control, monitoring, advanced data analysis, and reporting capabilities.
Understanding the specific control system is crucial for effective configuration testing. Different systems may require unique testing procedures and parameters.
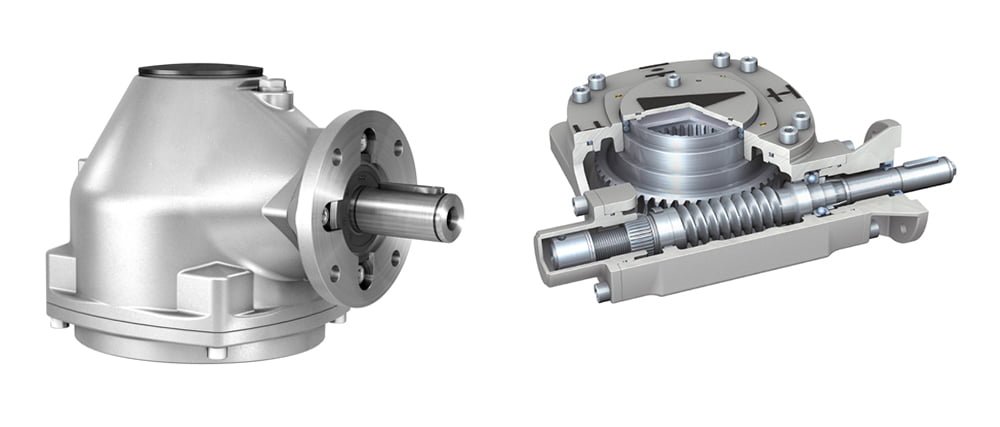
Key Components of Actuator Motors
Actuator motors are the driving force behind AUMA actuators, which convert electrical energy into mechanical motion. To master configuration testing, it’s essential to understand the key components of these motors, including:
1. Motor Windings:
Motor windings are coils of wire that generate a magnetic field when energized, producing the torque needed to move the actuator. Configuration testing should ensure that the windings are in good condition and receive the correct voltage and current.
2. Motor Bearings:
Bearings support the motor’s moving parts and reduce friction. During configuration testing, it’s essential to check for signs of wear or damage, as worn bearings can lead to decreased performance and increased energy consumption.
3. Motor Brushes:
Brushes transfer electrical power to the motor’s rotating components. During configuration testing, inspect the brushes for wear and replace them if necessary, as worn brushes can cause the motor to operate inefficiently.
Operators can ensure that their actuator motors function at peak performance by regularly inspecting and maintaining these key components.

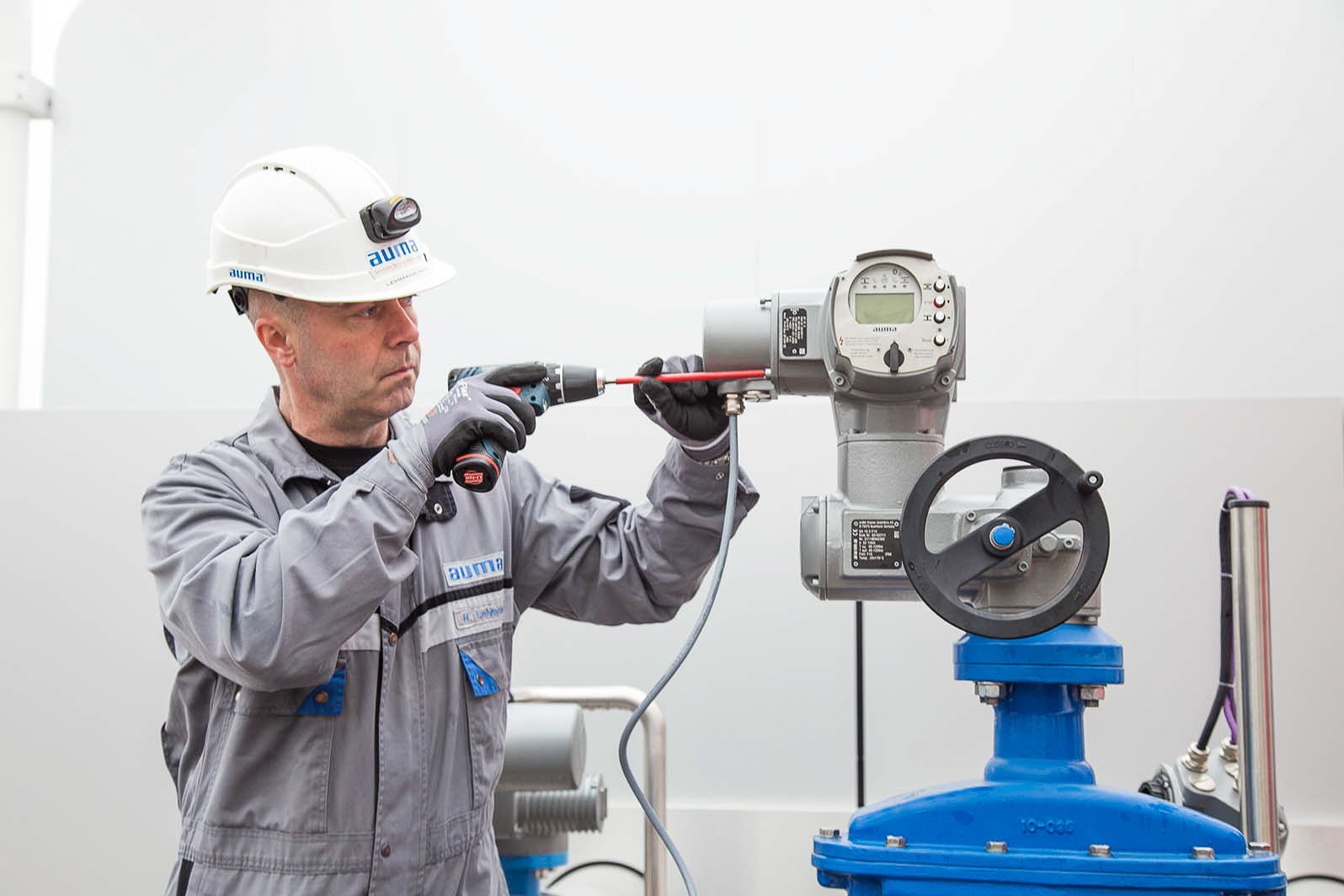
Step-by-Step Guide to Actuator Test Procedures
To conduct effective configuration testing, following a systematic approach that covers all aspects of actuator operation is essential.
Here is a step-by-step guide to AUMA actuator configuration test procedures:
1. Preparation:
Begin by gathering the necessary tools and equipment, including multimeters, torque wrenches, and any required documentation for the specific actuator model. Before starting the test, ensure the actuator is safely isolated from any power sources.
2. Visual Inspection:
Conduct a thorough visual inspection of the actuator, checking for signs of damage, wear, or corrosion. Pay particular attention to the motor windings, bearings, brushes, and any external components such as mounting brackets and couplings.
3. Electrical Testing:
Use a multimeter to verify that the actuator motor receives the correct voltage and current. Check the wiring for any signs of damage, wear, or loose connections.
4. Mechanical Testing:
Test the actuator’s torque output using a torque wrench, ensuring it meets the manufacturer’s specifications. Check the actuator’s mechanical components, such as gears and couplings, for signs of wear or damage.
5. Functional Testing:
Verify that the actuator is responding correctly to input signals from the control system. Ensure the actuator’s range of motion and operating speeds are within the manufacturer’s specifications.
6. Configuration Testing:
Verify that the actuator’s settings and parameters, such as limit switches and feedback mechanisms, are correctly configured. Make any necessary adjustments to ensure optimal performance.
7. Documentation:
Record the results of the tests, noting any issues identified and the steps taken to address them. Keep a detailed log of all configuration testing for future reference.
Following this step-by-step guide, operators can ensure that their AUMA actuators are correctly configured and operating at peak performance.
How to Test Actuator: Tools and Techniques
To conduct effective configuration testing, operators will need various tools and techniques at their disposal. Here are some essential tools and techniques for actuator testing:
1. Multimeters:
Multimeters are indispensable for testing electrical parameters, such as voltage and current. Operators should be familiar with using a multimeter to take accurate readings and diagnose potential issues.
2. Torque Wrenches:
Torque wrenches are essential for testing the actuator’s torque output, ensuring it is within the manufacturer’s specifications. Operators should know how to use a torque wrench and interpret the results.
3. Oscilloscopes:
Oscilloscopes are useful for analyzing the actuator’s electrical signals, such as input signals from the control system and output signals to the motor. Operators should be familiar with using an oscilloscope and interpreting the waveforms displayed.
4. Infrared Thermometers:
Infrared thermometers are useful for measuring the temperature of the actuator’s components during operation. This can help operators identify potential issues, such as overheating, which can cause damage and decrease performance.
In addition to these tools, operators should be familiar with various testing techniques, such as continuity testing, insulation resistance testing, and vibration analysis. By mastering these tools and techniques, operators can conduct comprehensive configuration testing to ensure optimal performance.

Troubleshooting Common Actuator Configuration Issues
During configuration testing, operators may encounter various issues that can impact actuator performance. Here are some common actuator configuration issues and their potential solutions:
1. Incorrect Voltage or Current:
If the actuator motor receives incorrect voltage or current, operators should first check the wiring and connections for any signs of damage, wear, or loose connections. If the issue persists, consult the manufacturer’s documentation for guidance on adjusting the voltage and current settings.
2. Worn Motor Components:
If the motor windings, bearings, or brushes show signs of wear or damage, operators should replace them as needed to ensure optimal performance. Consult the manufacturer’s documentation for guidance on replacing these components.
3. Inaccurate Torque Output:
If the actuator’s torque output is not within the manufacturer’s specifications, operators should first verify that the actuator’s mechanical components, such as gears and couplings, are in good condition. If the issue persists, consult the manufacturer’s documentation for guidance on adjusting the torque settings.
4. Incorrect Range of Motion or Operating Speeds:
If the actuator’s range of motion or operating speeds are not within the manufacturer’s specifications, operators should verify that the actuator’s settings and parameters are correctly configured. If the issue persists, consult the manufacturer’s documentation for guidance on adjusting these settings.
By troubleshooting and addressing these common issues, operators can ensure that their AUMA actuators operate at peak performance.
Optimizing Actuator Performance through Regular Testing
To maintain optimal performance and prolong the lifecycle of AUMA actuators, it is essential to conduct regular configuration testing. This proactive approach allows operators to identify and address potential issues before they escalate into more significant problems, ultimately saving time and money by reducing the likelihood of system failures and costly downtime.
Regular testing also helps operators stay familiar with the actuator’s components and settings, enabling them to make more informed decisions when adjusting parameters or troubleshooting issues.
By incorporating a regular testing schedule into their maintenance routines, operators can ensure that their AUMA actuators continue to perform at their best.
Conclusion: The Value of Mastering AUMA Actuator Configuration Testing
Mastering AUMA actuator configuration testing is essential for ensuring your valve automation systems’ optimal performance, safety, and longevity. By following this comprehensive guide, operators can develop a thorough understanding of actuator control systems, motors, and testing procedures, ultimately maximizing the value of their AUMA actuators.
By conducting regular testing and proactive maintenance, operators can identify and address potential issues early on, reducing the likelihood of system failures and costly downtime. In the long run, this can lead to significant cost savings and increased efficiency for the entire system.
Don’t hesitate to seek professional support and services from AUMA when necessary. Their expertise can be invaluable in ensuring your actuators’ proper configuration and testing. By mastering AUMA actuator configuration testing, operators can truly unlock the full potential of their valve automation systems.